D1.5 Alkynes
An alkyne is a hydrocarbon with one or more carbon-carbon triple bonds. Two carbon atoms joined by a triple bond are bound together by one σ bond and two π bonds. The general molecular formula of an alkyne with one triple bond is CnH2n-2. The alkyne has four hydrogen atoms fewer than the corresponding alkane with same number of carbons, and hence it has two degrees of unsaturation.
The suffix -yne is used to indicate the presence of a triple bond. The simplest alkyne is ethyne, C2H2, commonly called acetylene. The Lewis structure for ethyne is:
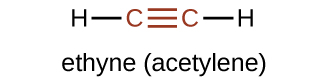
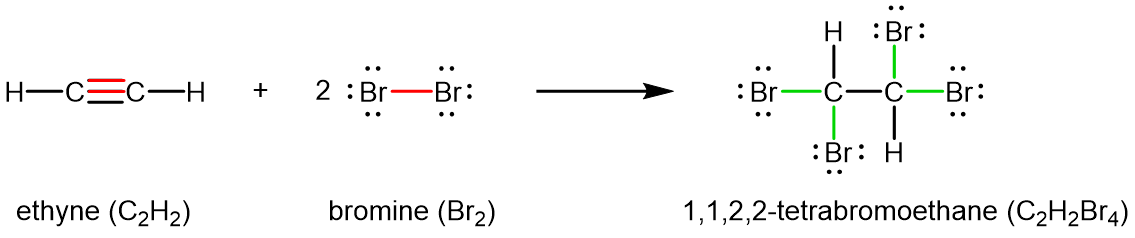
Chemically, alkynes have reactivity similar to alkenes. Since the C≡C functional group has two π bonds, alkynes can react with twice as much reagent in an addition reaction. For example, acetylene can react with bromine in the following reaction:
Exercise: Formulas, Multiple Bonds, and Rings
Exercise: Bond Lengths in Hydrocarbons
Please use this form to report any inconsistencies, errors, or other things you would like to change about this page. We appreciate your comments. 🙂 (Note that we cannot answer questions via the google form. If you have a question, please post it on Piazza.)

