D32.8 Radiometric Dating
Several radioisotopes have half-lives and other properties that make them useful for radiometric dating, the process of determining an object’s date of origin. The objects of interest can be geological formations, archaeological artifacts, or formerly living organisms. Radiometric dating has been responsible for many breakthrough scientific discoveries about the geological history of the earth, the evolution of life, and the history of human civilizations.
Radiometric Dating Using Carbon-14
Radiocarbon dating or carbon-14 dating can provide reasonably accurate dating of carbon-containing substances up to ~50,000 years old.
Naturally occurring carbon consists of three isotopes: 12C, which constitutes 99% of the carbon on earth; 13C, about 1% of the total; and 1 part per trillion (0.0000000001%) of 14C. 14C is formed in the upper atmosphere by the reaction of nitrogen atoms with neutrons:
All isotopes of carbon react with oxygen to produce CO2. In the atmosphere, the ratio of 14CO2 to 12CO2 has been nearly constant for a long time, as shown by analysis of carbon-containing gas samples trapped in Greenland ice sheets.
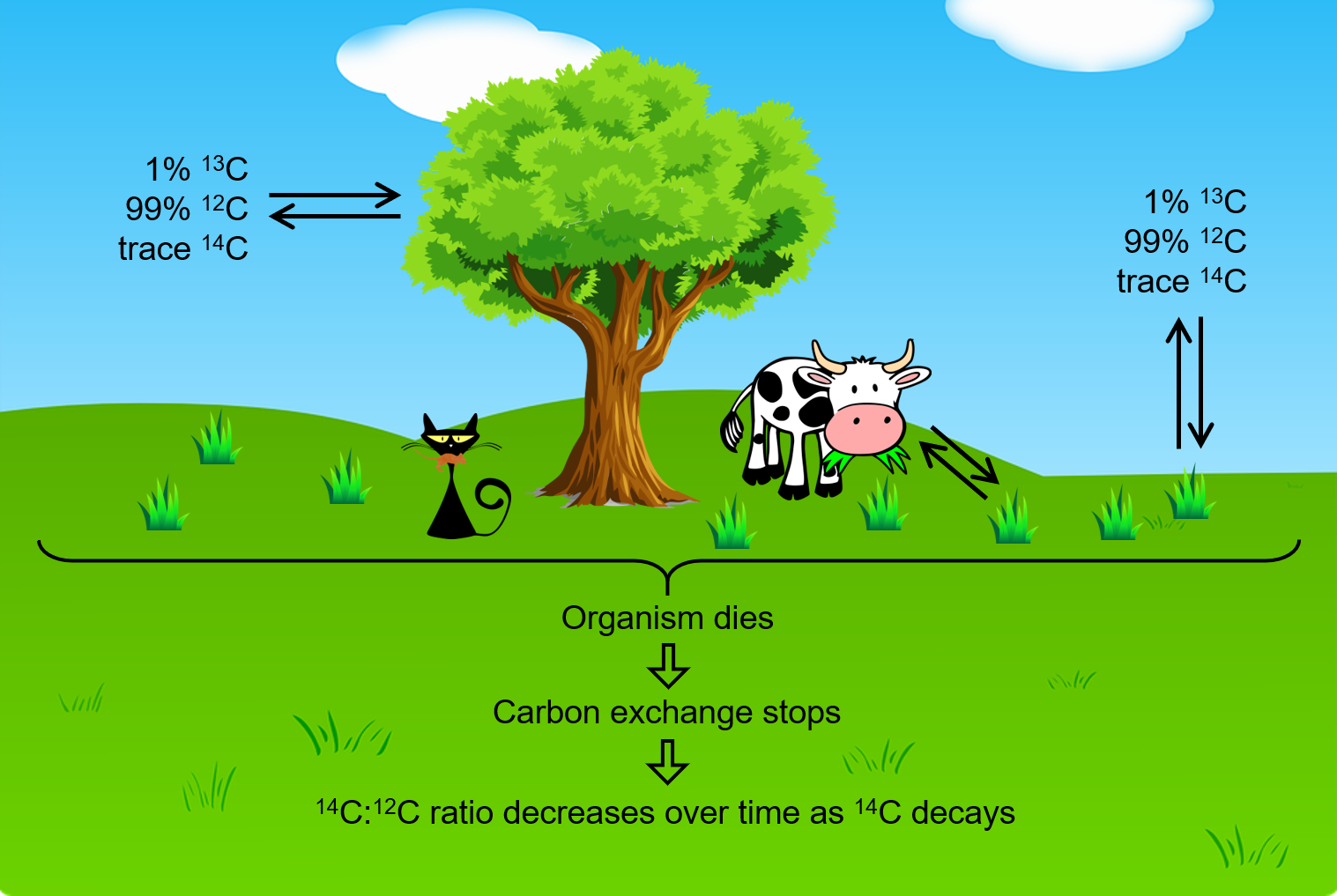
The incorporation of 14CO2, 13CO2 and 12CO2 into plants is a regular part of photosynthesis. Therefore, a living plant is constantly exchanging carbon with its environment, meaning that the 14C:12C ratio found in a living plant is the same as the 14C:12C ratio in the atmosphere. But when a plant dies, the carbon exchange with the atmosphere stops. Because 12C is a stable isotope and does not undergo radioactive decay, the amount of 12C in the dead plant does not change. However, 14C undergoes β decay with a half-life of 5730 years (β decay involves emission of an high energy electron from a nucleus):
Thus, the 14C:12C ratio gradually decreases after the plant dies, and this provides a measure of the time that has elapsed since the death of the plant. For example, if the 14C:12C ratio in a wooden object found in an archaeological site is half what it is in a living tree, this indicates that 5730 years have elapsed since the death of the tree from which the wooden object was made. Highly accurate determinations of 14C:12C ratios can be obtained from very small samples (as little as a milligram) by the use of a mass spectrometer.
This process works for other organisms as well, since they also constantly exchange carbon (by eating plants or eating others that eat plants) until they die.
Activity: Radiocarbon Dating
The accuracy of radiocarbon dating assumes that the 14C:12C ratio in a living plant is the same now as it was in an earlier era, but this is not always valid. For example, right now, due to the increasing accumulation of CO2 (largely 12CO2) in the atmosphere, caused by combustion of fossil fuels in which essentially all of the 14C has decayed, the 14C:12C ratio in our atmosphere is decreasing. This in turn affects the 14C:12C ratio in currently living organisms on earth. Fortunately, we can use other data, such as tree dating via examination of annual growth rings, to calculate correction factors. With these correction factors, more accurate dates can be determined. In general, radioactive dating only works for about 10 half-lives; therefore, the limit for carbon-14 dating is about 57,000 years.
Radiometric Dating Using Nuclides Other than Carbon-14
Radiometric dating using radioactive nuclides with half-lives longer than that of carbon-14 can date events older than 57,000 years ago.
For example, uranium-238 can be used to estimate the ages of some of the oldest rocks on earth. Since 238U has a half-life of 4.5 billion years, it takes that amount of time for half of the original 238U to decay by a series of nuclear reactions into 206Pb. In a rock sample that does not contain appreciable quantities of 208Pb, the most abundant isotope of lead, we can assume that lead was not present when the rock was formed. Therefore, by measuring and analyzing the ratio of 238U:206Pb, we can determine the age of the rock. This assumes that all of the 206Pb present came from the decay of 238U. If there is 206Pb from sources other than 238U, which is often indicated by the co-presence of other lead isotopes in the sample, it is necessary to make adjustments in the calculations.
Potassium-argon dating uses a similar method. 40K decays to form 40Ar with a half-life of 1.25 billion years. If a rock sample is crushed and the amount of 40Ar gas that escapes is measured, determination of the 40K:40Ar ratio yields the age of the rock. Other methods, such as rubidium-strontium dating (87Rb decays into 87Sr with a half-life of 48.8 billion years), operate on the same principle.
To estimate the lower limit for the earth’s age, scientists determine the age of various rocks and minerals, making the assumption that the earth is older than the oldest rocks and minerals in its crust. The oldest rocks on earth that has been dated are the Jack Hills zircons from Australia, found by uranium-lead dating to be almost 4.4 billion years old.
Please use this form to report any inconsistencies, errors, or other things you would like to change about this page. We appreciate your comments. 🙂

