Resume or Curriculum Vitae (CV)
Both a resume and CV should:
- be tailored for the graduate school program – this can be done through use of keywords, as well as order of sections and titles of sections (for example: Healthcare Experience, Research Experience, etc.)
- use bullet points with action verbs focused on strengths and skills
- represent you as the well-qualified applicant
- NOT include personal interests nor personal info (like picture, birthdate, marital status, nationality, etc.)
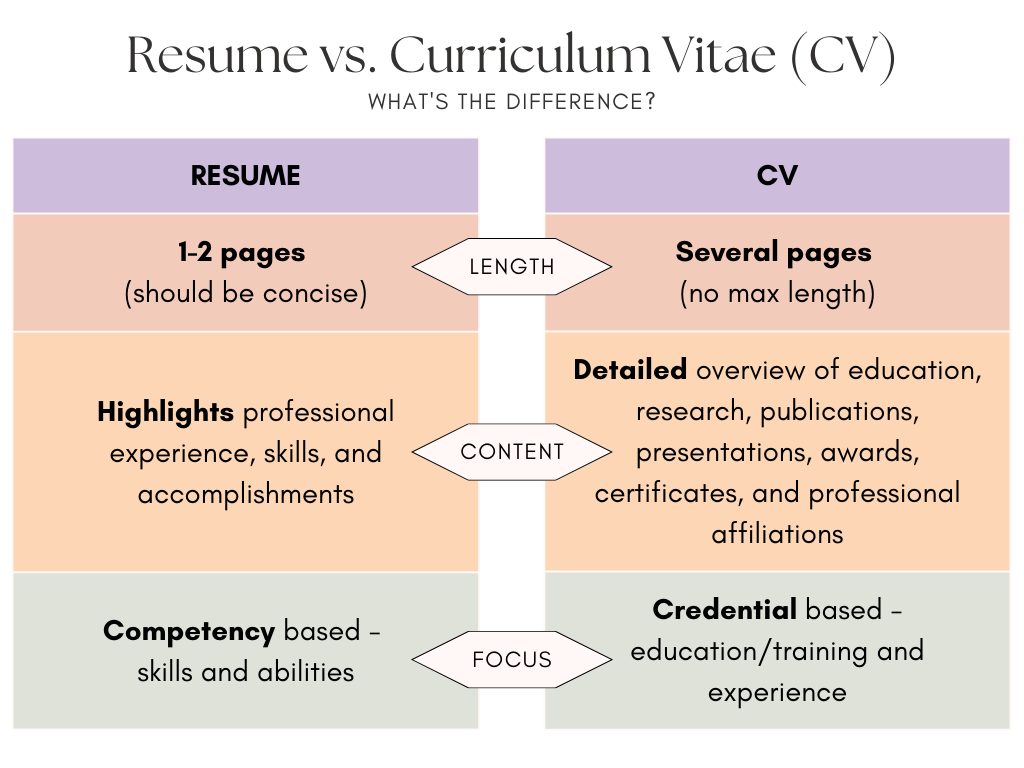
See the chart below to learn about the difference between a resume and a CV:
 ✅ HELPFUL TIP: If a graduate program allows you to submit either a resume or a CV, consider two factors when deciding which to submit:
✅ HELPFUL TIP: If a graduate program allows you to submit either a resume or a CV, consider two factors when deciding which to submit:
- Your qualifications: consider the key differences between a resume and CV (see chart above) and ask yourself which one will provide a better representation of who you are and how you will be a good fit for the program – resumes are best suited for candidates with significant work, volunteer, and/or leadership experience while CVs are ideal for individuals with research experience, publications, and/or a desire to highlight academic projects that relate to the program.
- The program’s focus: if the program is primarily focused on research (such as a PhD), then they might prefer a CV since it will include more information about your research experience. However, if the program emphasizes practical experience and skills, a resume may be more suitable.
Ultimately, the goal is to present your qualifications in a way that effectively highlights your fit for the program!
Support for creating or updating your resume or CV:
- SuccessWorks Support: Resume Support includes a free Canvas module to help you get started, resume feedback appointments, sample documents, and more!
- Writing Center Support: Resume Writing Tips, CV Writing Tips, and Make a Writing Appointment
- Converting Your Resume to a CV: A Step-by-Step Guide
