Lab 3 Background
Agarose Gel Imaging and Analysis
Agarose gels are commonly imaged using an ultraviolet (UV) transilluminator that emits UV light. However, because nucleic acids alone cannot be detected under UV light readily, ethidium bromide (EtBr), a fluorescent dye, is added to the DNA (In most cases, EtBr is added to the agarose gel and is then transferred onto DNA during gel electrophoresis).
EtBr is a small molecule that can intercalate between the bases of double-stranded nucleic acids. When exposed to UV light, the EtBr emits an orange color, and thus can be seen using a UV transilluminator. The intensity of the fluorescence is proportional to the mass of the DNA.
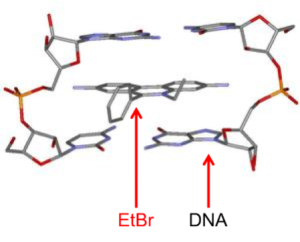
Caution: EtBr is a carcinogen. Make sure to wear gloves when handling it and keep it contained in the designated areas.
DNA Purification
DNA purification is needed to remove unwanted enzymes, buffers and other byproducts from previous reactions. DNA is purified using a spin column that contains a DNA-binding resin, which binds and retains DNA while other unwanted byproducts flow through the column. After washing the column, the DNA on the column is then eluted using an elution buffer.

