Unit 4: Fundamentals of Academic Essay Writing
32 Avoiding “Dumped Evidence”
Be careful to avoid “dumped” evidence
Integrating evidence, especially step three, can be a challenging part of the writing process. It may be tempting when writing a paragraph to simply “dump” several pieces of evidence, in the form of quotations or paraphrases, without any attempt to introduce or explain the evidence. Notice how the example below lacks integration.
Example:
In the example above, the writer has simply listed pieces of evidence one after the another, and the paragraph is devoid of the writer’s voice. The writer’s voice is needed to connect the ideas together into a coherent argument. The result is a lack of cohesion and there is no indication of how the ideas relate to each other.
Key Takeaway
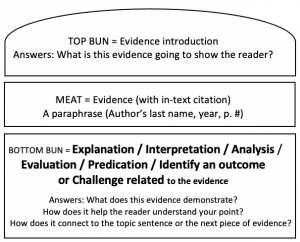
Remember: Effective writing is often described as clear thinking made visible. In this way, you need to make clear your analysis through YOUR VOICE: the buns / ICE so the reader can understand your thought process
Below is the “Research Hamburger” as a quick-guide to adding your voice.