M18Q6: E° and ΔG°, the Nernst Equation
Learning Objectives
- Calculate ΔG° and K from E°.
- Calculate E° from ΔG° or K for a redox reaction.
- Apply the Nernst equation to calculate the potential for a cell under non-standard state conditions or to calculate an unknown concentration in an electrochemical cell.
| Nernst Equation | - Interpret results from Nernst equation calculations to determine whether a reaction will form more reactants or products in order to achieve equilibrium.
| Key Concepts and Summary | Key Equations | Glossary | End of Section Exercises |
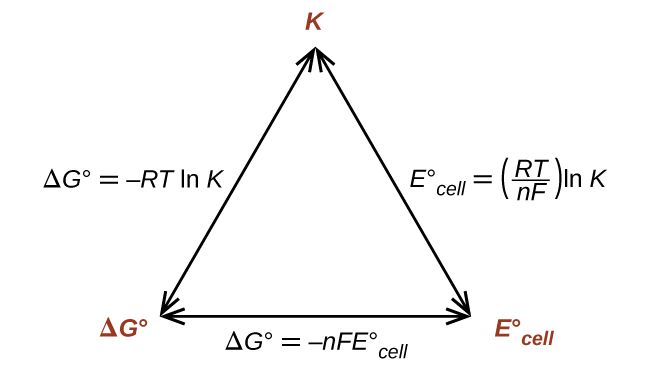
ΔG°, K°, and E°cell
We will now extend electrochemistry by determining the relationship between E°cell and the thermodynamics quantities such as ΔG° (Gibbs free energy) and K (the equilibrium constant).
In galvanic cells, chemical energy is converted into electrical energy, which can do work. The electrical work is the product of the charge transferred multiplied by the potential difference (voltage):
electrical work (J) = volts × charge in coulombs
The charge of 1 mole of electrons is given by Faraday’s constant (F):
F = (6.022 × 1023 ![]() ) × (1.66022 × 10-19
) × (1.66022 × 10-19 ![]() ) = 9.648 × 104
) = 9.648 × 104 ![]() = 9.648 × 104
= 9.648 × 104 ![]()
Hence, the total quantity of charge transferred is, where n is the number of moles of electrons for the balanced oxidation-reduction reaction:
total charge = moles e– × F = nF
This equation can be related to free energy with the following equation
ΔG = –nFEcell
If all the reactants and products are in their standard states, this becomes:
ΔG° = –nFE°cell
We can verify the signs are correct when we realize that n and F are positive constants and that galvanic cells, which have positive cell potentials, involve spontaneous reactions. Thus, spontaneous reactions, which have ΔG < 0, must have Ecell > 0.
This provides a way to relate standard cell potentials to equilibrium constants, since:
ΔG° = -RT ln(K)
–nFE° = -RT ln(K) or E°cell = ![]() ln(K)
ln(K)
Most of the time, the electrochemical reactions are run at standard temperature (298.15 K). Collecting terms at this temperature yields:
E°cell = ![]() ln(K) =
ln(K) = ![]() ln(K) =
ln(K) = ![]() ln(K)
ln(K)
where n is the number of moles of electrons. For historical reasons, the logarithm in equations involving cell potentials is often expressed using base 10 logarithms (log), which changes the constant by a factor of 2.303:
E°cell = ![]() log(K)
log(K)
Thus, if ΔG°, K, or E°cell is known or can be calculated, the other two quantities can be readily determined. The relationships are shown graphically in Figure 1.
Example 1
Equilibrium Constants, Standard Cell Potentials, and Standard Free Energy Changes
What is the standard free energy change and equilibrium constant for the following reaction at 25 °C?
2 Ag+(aq) + Fe(s) → 2 Ag(s) + Fe2+(aq)
Solution
The reaction involves an oxidation-reduction reaction, so the standard cell potential can be calculated using the E° reduction data in Appendix K.
Anode (oxidation): Fe(s) → Fe2+(aq) + 2 e– E°Fe2+/Fe = -0.44 V
Cathode (reduction): Ag+(aq) + e– → Ag(s) E°Ag+/Ag = +0.80 V
E°cell = E°cathode – E°anode = E°Ag+/Ag – E°Fe2+/Fe = +1.24 V
Remember that even though there are different numbers of electrons in each half-reaction, the cell potential for the cathode is not multiplied by two when determining the standard cell potential.
However, the number of electrons being exchanged does matter in the thermodynamic equations. The cathode reaction must be multiplied by 2 in order to have equal number of electrons exchanged, therefore n = 2. The equilibrium constant can then be calculated:
E°cell = ![]() ln(K) =
ln(K) = ![]() ln{K} =
ln{K} = ![]() ln(K)
ln(K)
K = e(n)(E°cell)/(0.0257 V) = e(2)(1.24 V)/(0.0257 V) = 8.10 × 1041
The standard free energy can then be calculated:
ΔG° = –nFE°cell
ΔG° = -(2)(96485 ![]() )(1.24 V) = -2.39 × 105 J/mol = -239 kJ/mol
)(1.24 V) = -2.39 × 105 J/mol = -239 kJ/mol
Check your answer: A positive standard cell potential means a spontaneous reaction under standard conditions, so the standard free energy change should be negative, and an equilibrium constant should be >1.
Check Your Learning
What is the standard free energy change and the equilibrium constant for the following reaction at room temperature? Is the reaction spontaneous?
Sn(s) + 2 Cu2+(aq) → Sn2+(aq) + 2 Cu+(aq)
Answer:
Spontaneous
n = 2; Eºcell = +0.30 V; ΔG° = -57.9 kJ/mol; K = 1.38 × 1010
Now that the connection has been made between the free energy and cell potentials, nonstandard concentrations follow. Recall that
ΔG = ΔG° + RT ln(Q)
where Q is the reaction quotient. Converting to cell potentials:
–nFEcell = –nFE°cell + RT ln(Q)
Ecell = E°cell – ![]() ln(Q)
ln(Q)
With the Nernst equation, it is possible to calculate the cell potential at nonstandard conditions. This adjustment is necessary because potentials determined under different conditions will have different values.
Example 2
Cell Potentials at Nonstandard Conditions
Consider the following reaction at room temperature:
Co(s) + Fe2+(aq, 1.94 M) → Co2+(aq, 0.15 M) + Fe(s)
Is the process spontaneous?
Solution
There are two ways to solve the problem. If the thermodynamic information in Appendix F were available, you could calculate the free energy change. If the free energy change is negative, the process is spontaneous. The other approach, which we will use, requires information like that given in Appendix K. Using those data, the cell potential can be determined. If the cell potential is positive, the process is spontaneous. Collecting information from Appendix K and the problem,
Anode (oxidation): Co(s) → Co2+(aq) + 2 e– E°Co2+/Co = -0.28 V
Cathode (reduction): Fe2+(aq) + 2 e– → Fe(s) E°Fe2+/Fe = -0.45 V
E°cell = Eºcathode – E°anode = -0.45 V – (-0.28 V) = -0.17 V
The process is not spontaneous under standard conditions. Using the Nernst equation and the concentrations stated in the problem and n = 2,
Q = ![]() = 0.077
= 0.077
Ecell = E°cell – ![]() ln(Q) = (-0.17 V) –
ln(Q) = (-0.17 V) – ![]() ln(0.077) = -0.14 V
ln(0.077) = -0.14 V
E°cell is negative so the process is nonspontaneous.
Check Your Learning
What is the cell potential for the following reaction at room temperature?
Al(s) | Al3+(aq, 0.15 M) || Cu2+(aq, 0.025 M) | Cu(s)
What are the values of n and Q for the overall reaction? Is the reaction spontaneous under these conditions?
Answer:
n = 6; Q = 1440; Ecell = +1.99 V, spontaneous. (Hint: If you are not calculating the correct value for Q, double check that you are including coefficients of aqueous species as exponents in Q!)
Finally, we will take a brief look at a special type of cell called a concentration cell. In a concentration cell, the electrodes are the same material and the half-cells differ only in concentration. A concentration cell acts to dilute the more concentrated solution and concentrate the more dilute solution, creating a voltage as the cell reaches an equilibrium. This is achieved by transferring the electrons from the cell with the lower concentration to the cell with the higher concentration. Another way to think about it is that since one or both compartments is not standard, the cell potentials will be unequal; therefore, there will be a potential difference, which can be determined with the aid of the Nernst equation.
In Figure 2, a nickel concentration cell is shown, consisting of a more dilute Ni2+(aq) solution in the left cell and a more concentrated Ni2+(aq) solution on the right. A redox reaction will occur until the two solution are equal concentrations, so the left cell must increase its Ni2+(aq) concentration and the right cell must lower its Ni2+(aq) concentration until both cells have the same Ni2+(aq) concentration.
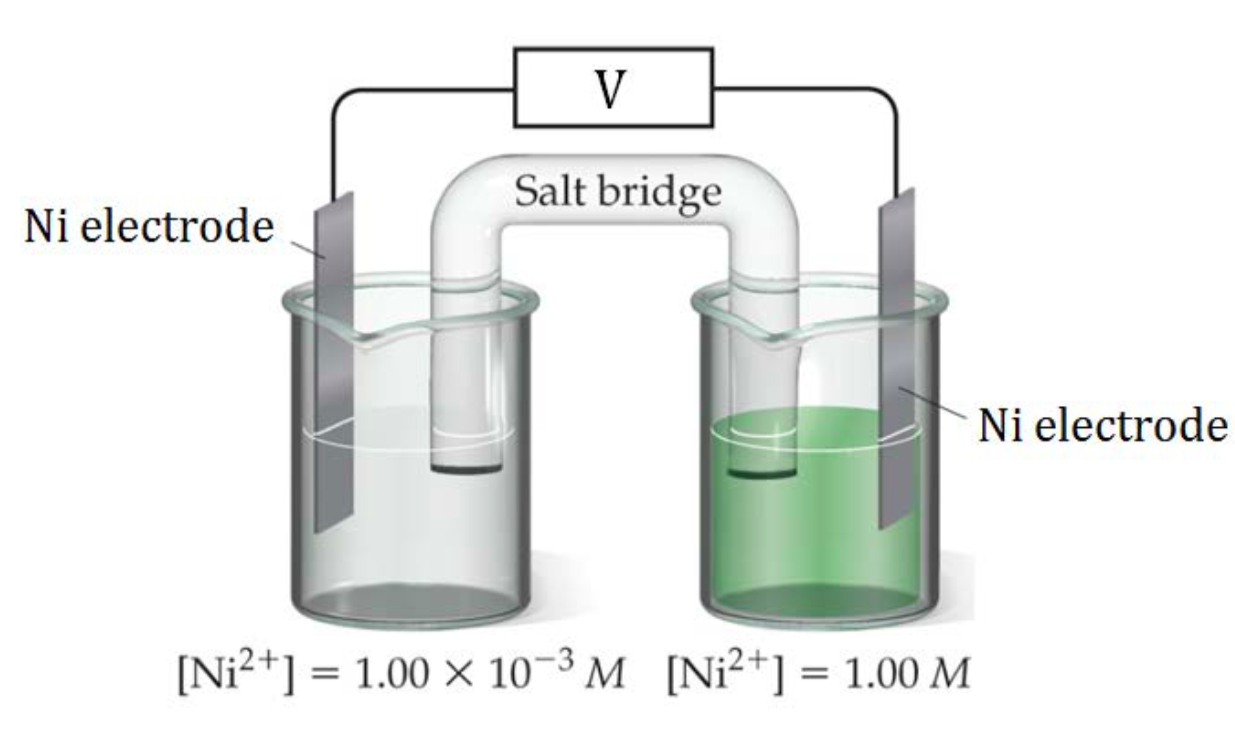
| Left Cell | Must increase [Ni2+] so reaction occurring is: | Ni(s) → Ni2+ + 2 e– | This is an oxidation reaction so the left side is the anode |
| Right Cell | Must lower [Ni2+] so reaction occurring is: | Ni2+ + 2 e– → Ni(s) | This is a reduction reaction so the left side is the cathode. |
The potential for a concentration cell can be determined with the following equation:
Ecell = E°cell – ![]() ln
ln ![]()
Example 3
Concentration Cells
What is the cell potential of the concentration cell at 298 K described by
Zn(s) | Zn2+(aq, 0.10 M) || Zn2+(aq, 0.50 M) | Zn(s)
Solution
From the information given:
| Anode: | Zn(s) | ⟶ | Zn2+(aq, 0.10 M) + 2 e– | E°anode = -0.76 V |
| Cathode: | Zn2+(aq, 0.50 M) + 2 e– | ⟶ | Zn(s) | E°cathode = -0.76 V |
| Overall: | Zn2+(aq, 0.50 M) | ⟶ | Zn2+(aq, 0.10 M) | E°cell = 0.00 V |
The standard cell potential is zero because the anode and cathode involve the same reaction; only the concentration of Zn2+ changes. Substituting into the Nernst equation,
Ecell = E°cell – ![]() ln
ln ![]() = +0.021 V
= +0.021 V
and the process is spontaneous at these conditions.
Check your answer: In a concentration cell, the standard cell potential will always be zero. To get a positive cell potential (spontaneous process) the reaction quotient Q must be < 1. Q < 1 in this case, so the process is spontaneous.
Check Your Learning
What value of Q for the previous concentration cell would result in a voltage of 0.10 V? If the concentration of zinc ion at the cathode was 0.50 M, what was the concentration at the anode?
Answer:
Q = 4.1 × 10-4; [Zn2+]anode = 2.1 × 10−4 M.
Demonstration: Concentration Cell
Set up. Two beakers are connected as an electrochemical cell.
Step 1: Both beakers contain both a Cu(s) electrode and a 1.0 M CuSO4(aq) solution. The electrodes are connected with a voltmeter and the beakers are connected with a KNO3(aq) salt bridge to complete the circuit.
Step 2: The solutions in the left beaker is changed, where the left beaker still contains a Cu(s) electrode but now a 0.001 M CuSO4(aq) solution. The right beaker still contains a Cu(s) electrode and a 1.0 M CuSO4(aq) solution. The electrodes are connected with a voltmeter and the beakers are connected with a KNO3 salt bridge to complete the circuit.
Step 3: A 1.0 M Na2S(aq) solution is added to the 0.001 M CuSO4(aq) beaker.
Prediction. What do you predict the voltage will be in each step? Will the voltage be the same or different in each step?
Explanation: Step 1: When the same 1.0 M CuSO4(aq) solution is in each beaker, the voltmeter measures 0.0 V. Since both halves of the cell are equivalent, no electrons flow between the beakers.
Step 2: When the left beaker is replaced with a 0.001 M CuSO4(aq) solution, the voltmeter initially measures 0.064 V, which does not significantly change. If enough time is given, electrons will flow from the Cu(s) electrode on the left (the anode) to the Cu(s) electrode on the right (the cathode), increasing the Cu2+(aq) concentration in the left beaker and decreasing the Cu2+(aq) concentration in the right beaker. As they come closer to equal, the voltage decreases until it would measure 0.0 V when the concentrations are equal.
Step 3: When the Na2S(aq) is added, a brown precipitate of CuS(s) appears, and the voltage increases significantly to around 0.5 V. Adding the S2-(aq) pulls Cu2+(aq) ions out of solution in the left beaker, causing the Cu(s) electrode to dissolve and create more Cu2+(aq) ions, increasing the flow of electrons.
Key Concepts and Summary
In this section, we bring together our knowledge of voltaic cells to look at the free energy (ΔG) and electrical potential created in a system at equilibrium as well as a system not at equilibrium. In order to complete these calculations, we often use Faraday’s constant (9.648 × 104 ![]() ), which is the charge of 1 mole of electrons. Using Figure 1, the quantities ΔGº, K, and Eºcell are connected. If you know one of these quantities, you can calculate the other two. We can also use the reaction quotient, Q, to study a system where its progress towards equilibrium is unknown using the Nernst equation. We apply the Nernst equation to a particular type of cell called a concentration cell, where the electrodes are the same material but the aqueous solutions differ in their concentration. In this case, the anode is the half-cell with the lower concentration and the cathode is the half-cell with the higher concentration.
), which is the charge of 1 mole of electrons. Using Figure 1, the quantities ΔGº, K, and Eºcell are connected. If you know one of these quantities, you can calculate the other two. We can also use the reaction quotient, Q, to study a system where its progress towards equilibrium is unknown using the Nernst equation. We apply the Nernst equation to a particular type of cell called a concentration cell, where the electrodes are the same material but the aqueous solutions differ in their concentration. In this case, the anode is the half-cell with the lower concentration and the cathode is the half-cell with the higher concentration.
Key Equations
- electrical work (J) = volts × charge in coulombs
- total charge = moles e– × F = nF
- ΔG° = –nFE°cell
- ΔG° = -RT ln K
- E°cell =
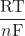 ln(K)
ln(K) - E°cell =
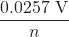 ln(K) (at 298.15 K)
ln(K) (at 298.15 K) - Ecell = E°cell –
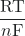 ln(Q)
ln(Q) - Ecell = E°cell –
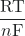 ln
ln ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \left(\dfrac{[\text{anode}]}{[\text{cathode}]}\right)](https://wisc.pb.unizin.org/app/uploads/quicklatex/quicklatex.com-44fa0d86deaa48357e9b140dbb0a2940_l3.png) (for a concentration cell)
(for a concentration cell)
Glossary
- concentration cell
- a voltaic cell where the electrodes are the same material, but the concentration of the aqueous solutions differ in concentration
- Faraday’s constant (F)
- the charge of 1 mole of electrons, 9.648 × 104
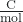
- Nernst equation
- an equation used to calculate the cell potential at nonstandard conditions
Chemistry End of Section Exercises
- For the standard cell potentials given here, determine the ΔG° for the cell in kJ/mol.
- 0.000 V, n = 2
- +0.434 V, n = 2
- −2.439 V, n = 1
- For the ΔG° values given here, determine the standard cell potential for the cell.
- 12 kJ/mol, n = 3
- −45 kJ/mol, n = 1
- Determine the standard cell potential and the cell potential under the stated conditions for the electrochemical reactions described here. State whether each is spontaneous or nonspontaneous under each set of conditions at 298.15 K.
- Hg(ℓ) + S2-(aq, 0.10 M) + 2 Ag+(aq, 0.25 M) ⇌ 2 Ag(s) + HgS(s)
- The galvanic cell made from a half-cell consisting of an aluminum electrode in 0.015 M aluminum nitrate solution and a half-cell consisting of a nickel electrode in 0.25 M nickel(II) nitrate solution.
- The cell made of a half-cell in which 1.0 M aqueous bromine is oxidized to 0.11 M bromide ion and a half-cell in which aluminum ion at 0.023 M is reduced to aluminum metal. Assume the standard reduction potential for Br2(ℓ) is the same as that of Br2(aq).
- Determine ΔG and ΔG° for each of the reactions in exercise 3.
- Using the following electrochemical data
Half-Reaction E° (V) Pb2+(aq) + 2 e– → Pb(s) -0.13 Fe3+(aq) + e– → Fe2+(aq) +0.77 to calculate ΔG° for the electrochemical cell described below.
Pb(s)| Pb2+(aq)|| Fe3+(aq)| Fe2+(aq)| Pt(s) - Given the following standard reduction potentials, calculate the solubility product, Ksp, of AgCN at 25 °C.
Ag+(aq) + e– → Ag(s) E° = 0.80 V AgCN(s) + e– → Ag(s) + CN–(aq) E° = –0.01 V - Calculate E at 298 K for a cell constructed using Cu/Cu2+ (1.0 M) and Ag/Ag+ (1.0 × 10-4 M). The standard reduction potentials are:
Cu2+(aq) + 2 e– → Cu(s) E° = +0.34 V
Ag+(aq) + e– → Ag(s) E° = +0.80V - Consider a voltaic cell based upon the following electrochemical reaction:
3 Ag+(aq) + Cr(s) ⇌ 3 Ag(s) + Cr3+(aq)
which has a standard cell potential, E°cell = 1.539 V. Calculate [Ag+] when [Cr3+] = 1.70 M and the measured cell potential is 1.565 V. The cell is operating at 298 K.
- Consider a voltaic cell based upon the following electrochemical reaction:
2 Fe3+(aq) + Cu(s) ⇌ 2 Fe2+(aq) + Cu2+(aq)
which has a stand cell potential, E°cell = 0.434 V. What is the cell potential, in volts, measured at 240 °C when [Fe2+] = 1.00 M, [Fe3+] = 2.40 M, and [Cu2+] = 2.20 M?
- An electrochemical cell is constructed according to the following chemical equation
2 Al(s) + 3 Fe2+(aq) → 2 Al3+(aq) + 3 Fe(s) E° = 1.30 V
What would be the reading on a voltmeter connected between the anode and cathode if [Fe2+] = 0.100 M and [Al3+] = 0.500 M at 298 K?
- The cell potential of a Zn-H+ cell is 0.45 V at 25°C when [Zn2+] = 1.0 M and the partial pressure of H2 is 1.0 atm. What is the pH of the cathode cell? Will changing the pH of the cathode cell effect the cell potential?
- The measured voltage of the cell below is 1.02 V at 25 °C.
Pt(s) | H2 (1.0 atm) | H+(aq) || Ag+(1.0 M) | Ag(s)
Calculate the pH of the solution given the following electrochemical data.
Half-Reaction E° (V) 2 H+(aq) + 2 e– → H2(g) 0.00 Ag+(aq) + e– → Ag(s) +0.80 - Which of the following statements are always true for a redox reaction that has reached equilibrium? Select all that apply.
- Q = 1
- ΔG = 0
- E = E°
- For the following reaction,
Co(s) + Sn2+(aq) → Sn(s) + Co2+(aq)
which of the following processes will Ecell for a voltaic cell increase? Select all that apply.
- Increase in the cell temperature
- Increase in the concentration of Sn2+
- Increase in the concentration of Co2+
- Consider a voltaic cell with the following reaction.
Cu2+(1M, aq) + Zn(s) → Zn2+(1M, aq) + Cu(s) E° = 1.10 V
As the cell reaction proceeds, what happens to the value of ΔG?
- It will become a bigger positive value.
- It will become a smaller positive value.
- It will become a bigger negative value.
- It will become a smaller negative value.
- It will not change as ΔG is constant at constant temperature.
- Consider the standard reduction potentials below
Al3+(aq) + 3e– → Al(s) E° = -1.66 V Ni2+(aq) + 2e– → Ni(s) E° = -0.25 V 2 H+(aq) + 2 e– → H2(g) E° = 0.00 V Ag+(aq) + e– → Ag(s) E° = +0.80 V Ce4+(aq) + e– → Ce3+(aq) E° = +1.61 V - The most powerful oxidizing agent in the list above is:
- The combination of which two substances would result in a redox reaction with the most negative ΔG°?
- Consider the standard reduction potentials below
Cd2+(aq) + 2e– → Cd(s) E° = -0.40 V Ag+(aq) + e– → Ag(s) E° = +0.80 V Fe2+(aq) + 2 e– → Fe(s) E° = -0.44 V Mg2+(aq) + 2e– → Mg(s) E° = -2.36 V Cu2+(aq) + 2e– → Cu(s) E° = +0.34 V - For which of the following combinations would a spontaneous reaction be observed?
- A strip of Mg(s) placed in a test tube containing a strip of Cu(s)
- A strip of Mg(s) placed in a test tube containing Cu(NO3)2(aq)
- Mg(NO3)2 (aq) placed in a test tube containing Cu(NO3)2(aq)
- A strip of Cu(s) placed in a test tube containing Fe(NO3)2(aq)
- A strip of Fe(s) placed in a test tube containing Mg(NO3)2(aq)
- Which of the following would result in a galvanic cell with the largest value of E°?
- Cd(s) | Cd2+(aq) || Cu2+(aq) | Cu(s)
- Fe(s) | Fe2+(aq) || Cu2+(aq) | Cu(s)
- Mg(s) | Mg2+(aq) || Ag+(aq) | Ag(s)
- Cu(s) | Cu2+(aq) || Mg2+(aq) | Mg(s)
- Cd(s) | Cd2+(aq) || Mg2+(aq) | Mg(s)
- Determine ΔG° for the redox reaction:
Fe(s) + 2 Ag+(aq) → Fe2+(aq) + 2 Ag(s) ΔG° = ?
- For which of the following combinations would a spontaneous reaction be observed?
- Which one of the following is consistent with a dead battery (an electrochemical cell at equilibrium)?
- ΔG = 0, Ecell = 0, Q = K
- ΔG < 0, Ecell > 0, Q < K
- ΔG = 0, Ecell < 0, Q = K
- ΔG > 0, Ecell < 0, Q < K
- ΔG > 0, Ecell = 0, Q > K
Answers to Chemistry End of Section Exercises
- (a) 0 kJ/mol; (b) −83.7 kJ/mol; (c) +235.3 kJ/mol
- (a) E° = -0.0414 V; (b) E° = 0.466 V
- (a) standard cell potential: 1.50 V, spontaneous; cell potential under stated conditions: 1.43 V, spontaneous
(b) standard cell potential: 1.426 V, spontaneous; cell potential under stated conditions: 1.444 V, spontaneous
(c) standard cell potential: −2.749 V, nonspontaneous; cell potential under stated conditions: −2.838 V, nonspontaneous - (a) ΔG° = -289 kJ/mol; ΔG = -277 kJ/mol
(b) ΔG° = -813 kJ/mol; ΔG = -818 kJ/mol
(c) ΔG° = 1590 kJ/mol; ΔG = 1643 kJ/mol - ΔG° = -1.7 × 102 kJ/mol
- Ksp = 2.0 × 10–14
- E = +0.22 V
- [Ag+] = 3.28 M
- E = 0.455 V
- 1.28 V
- pH = 5.27; yes
- pH = 3.72
- B
- B
- D
- (a) Ce4+(aq); (b) Al(s) + Ce4+(aq)
- (a) B; (b) C; (c) -240 kJ/mol
- A
Please use this form to report any inconsistencies, errors, or other things you would like to change about this page. We appreciate your comments. 🙂

