D42.3 Primary Batteries
Primary batteries are single-use batteries that cannot be recharged.
Zinc-Carbon Battery
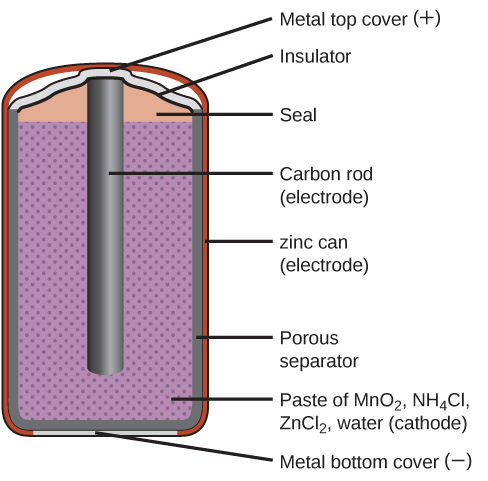
A common primary battery is the dry cell, which is a zinc-carbon battery. The zinc serves as both a container and the negative electrode (anode). The positive electrode (cathode) is a rod made of carbon that is surrounded by a paste of manganese(IV) oxide, zinc chloride, ammonium chloride, carbon powder, and a small quantity of water.
The reaction at the anode can be represented as the oxidation of zinc:
The reaction at the cathode is more complicated, in part because more than one reduction reaction is occurring. The series of reactions that occurs at the cathode is approximately:
The overall reaction for the zinc–carbon battery can be represented as:
The cell potential is about 1.5 V initially, and decreases as the battery is used. As the zinc container oxidizes, its contents eventually leak out, so this type of battery should not be left in any electrical device for extended periods.
The voltage delivered by a battery is the same regardless of the size of a battery. For this reason, D, C, A, AA, and AAA batteries all have the same voltage. However, larger batteries can deliver more moles of electrons and will therefore last longer if powering the same device.
Alkaline Battery
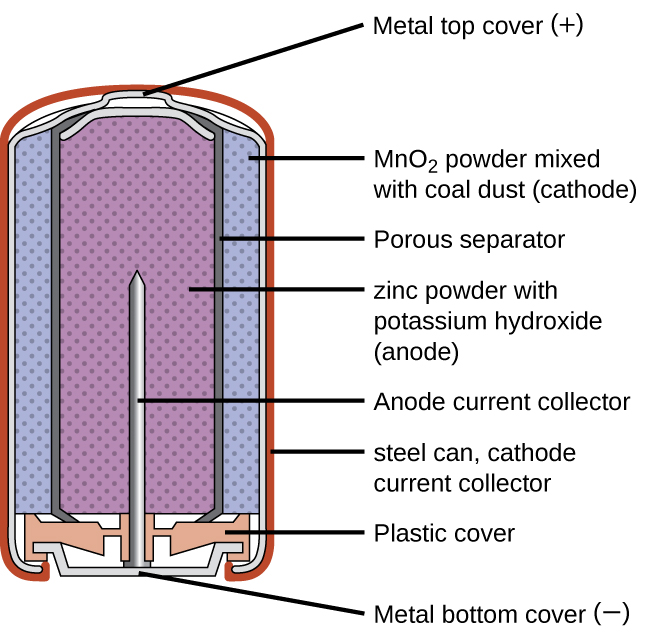
Alkaline batteries were developed in the 1950s partly to address some of the performance issues with zinc–carbon dry cells, and are manufactured to be their exact replacements. As their name suggests, these types of batteries use alkaline electrolytes, often potassium hydroxide.
The reactions are:
| Oxidation (anode): | Zn(s) + 2 OH–(aq) | ⟶ | ZnO(s) + H2O(ℓ) + 2 e– | E°anode = -1.28 V |
| Reduction (cathode): | 2 MnO2(s) + H2O(ℓ) + 2 e– | ⟶ | Mn2O3(s) + 2 OH–(aq) | E°cathode = +0.15 V |
| overall: | Zn(s) + 2 MnO2(s) | ⟶ | ZnO(s) + Mn2O3(s) | E°cell = +1.43 V |
An alkaline battery can deliver about three to five times the energy of a zinc-carbon dry cell of similar size. Alkaline batteries sometimes leak potassium hydroxide, so these should also be removed from devices for long-term storage. While some alkaline batteries are rechargeable, most are not. Attempts to recharge an alkaline battery that is not rechargeable often leads to rupture of the battery and leakage of the potassium hydroxide electrolyte.
Please use this form to report any inconsistencies, errors, or other things you would like to change about this page. We appreciate your comments. 🙂

