Hausa
About Hausa
Hausa is the largest West African language, and the predominant language of northern Nigeria and southern Niger. It is spoken as a first language by about half of the population of Niger, and one-fifth of the population of Nigeria. Hausa is the most important indigenous lingua franca (common language adopted between people who speak different native languages) in West and Central Africa and is spoken as far east as Sudan. Although estimates vary, roughly 50 million people speak Hausa as a first or second language. Hausa is a member of the Chadic group of languages, more closely related to Arabic, Hebrew, and Berber than most other languages of sub-Saharan Africa. Unlike English, it is a tonal language consisting of two tone levels, high and low, and a combination falling tone.
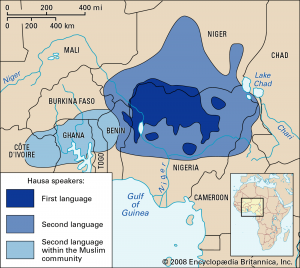
Hausa was first written in an Arabic script, ajami, but since about 1912, Roman script, boko, has become more common. Due to Arabic influence, almost one quarter of the words in Hausa are borrowed from Arabic. Interestingly, numerous radio stations including BBC, Radio France International, and Voice of America broadcast in Hausa.
Sources:
Al Jazeera: Warning Sounded over fate of Africa’s Hausa language. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ug6hFsIlCDM
https://www.worldatlas.com/articles/who-are-the-hausa-people.html
https://www.britannica.com/topic/Hausa-language
Kraft, C.H. (1973). Hausa.

