Lingala
About Lingala
Belonging to the Niger-Congo language family, Lingala is a Central Bantu language spoken in Sub-Saharan Africa. Lingala and its dialects are spoken from Cameroon to the most Southern region if DR Congo. The language originates from the Bangala who were tradesmen and riverine people of Mongala, Ngiri and the Ubangi rivers.
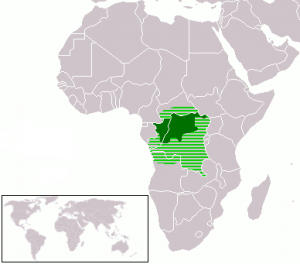
Between the DR Congo and the Republic of Congo alone, where it is a national language, over 58 million people speak Lingala. Additionally, it is spoken in Northwestern Angola, eastern Gabon, southern Central African Republic, and southwestern Sudan. About 25-38% of the Congolese population in the DRC speaks Lingala along with one of the other four national languages (i.e.: Kiswahili, Kikongo or Tshiluba). It is also a dominant lingua franca in many of the Western Provinces of the DRC. In Congo-Brazzaville, it is mainly the lingua franca in three major cities.
While there is no one Lingala culture in the region, the various Bangala subcultures that exist are reflected in Congolese music and dances from the region.
Resources
- National African Language Resource Center (NALRC), Lingala, Accessed on June 16 2021, https://nalrc.indiana.edu/doc/brochures/lingala.pdf
- Wikimedia Commons, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:LanguageMap-Lingala-Larger_Location.png

