Manding (Bambara, Dyula, & Malinké)
About the Manding Languages
What is Manding? What are the Manding Languages?
Manding, or the Manding languages, is a language-dialect continuum that is spoken across West Africa. Manding is found within the Mande language family and is known by various names depending on where it is spoken and by whom: Bambara/Bamana/Bamanakan, Dyula/Jula/Dioula, Maninka/Malinké, Mandinka, Mandingo, Mandekekan.
Wait… so is Manding one language? Or many languages?
For sociolinguistic reasons, native speakers usually refer to Manding by the name of the particular dialect spoken in their community. The three Eastern varieties of Manding– Bambara, Dyula, and Maninka– are highly mutually intelligible with each other, similar to the relationship between English from the US and UK or Spanish from Spain or Latin America. While the Western varieties of Manding spoken in the Gambia, Guinea-Bissau, and Senegal include Mandingo and Mandinka, these forms of Manding are not fully mutually intelligible with their Eastern counterparts.
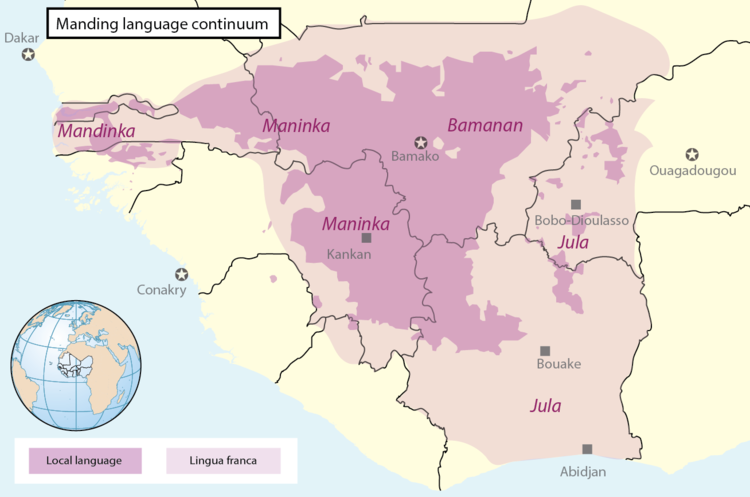
So which version of Manding should I learn?
That depends! Learning any one variety of Manding will allow you to be understood in many places, and will also form a basis for you to learn and understand other varieties. However, you may want to learn the dialect of Manding that is more relevant to you and the country you are visiting. Eastern Manding is known as Bambara in Mali, Dyula in Burkina Faso and Cote d’Ivoire, and Malinké in Guinea. Western Manding is known as Mandinka in the Gambia. This particular chapter focuses on studying and understanding Eastern Manding, including Bambara, Dyula, and Malinké.
Works Cited:
Donaldson, Coleman. “Resources.” An Ka Taa. 2019. https://www.ankataa.com/resources
Donaldson, Coleman. (2018, December 30). Map of the Manding language continuum. Zenodo. http://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.2528947

